1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| #include "xlinux.h"
static int xlinux_probe(struct pci_dev *pdev, const struct pci_device_id *id) {
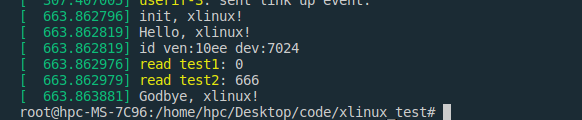
printk(KERN_INFO "Hello,device!\n");
printk(KERN_INFO "id ven:%x dev:%x\n", id->vendor, id->device);
int node;
int result = -ENOMEM;
node = dev_to_node(&pdev->dev);
if (node == NUMA_NO_NODE) set_dev_node(&pdev->dev, first_memory_node);
struct xlinux_dev *xlinux_dev = kzalloc_node(sizeof(*xlinux_dev), GFP_KERNEL, node);
if (!xlinux_dev) return -ENOMEM;
pci_set_drvdata(pdev, xlinux_dev);
if (pci_enable_device_mem(pdev)) return result;
pci_set_master(pdev);
int size = pci_resource_len(pdev, 0);
phys_addr_t phy_addr = pci_resource_start(pdev, 0);
unsigned long flag = pci_resource_flags(pdev, 0);
xlinux_dev->bar = ioremap(phy_addr, size);
printk(KERN_INFO "****BAR INFO****\n");
printk(KERN_INFO "BAR0 start:0x%llx\n", phy_addr);
printk(KERN_INFO "BAR0 size:%d\n", size);
printk(KERN_INFO "BAR0 flag:0x%lx\n", flag);
printk(KERN_INFO "virt add:0x%p\n", xlinux_dev->bar);
printk(KERN_INFO "read test1: %d\n", readl(xlinux_dev->bar + 2000));
writel(666, xlinux_dev->bar + 2000);
printk(KERN_INFO "read test2: %d\n", readl(xlinux_dev->bar + 2000));
return 0;
}
static void xlinux_remove(struct pci_dev *pdev) {
printk(KERN_INFO "Godbye, device!\n");
struct xlinux_dev *xlinux_dev = pci_get_drvdata(pdev);
iounmap(xlinux_dev->bar);
kfree(xlinux_dev);
}
static const struct pci_device_id xlinux_id_table[] = {{.vendor = 0x10ee, .device = 0x7024, .subvendor = PCI_ANY_ID, .subdevice = PCI_ANY_ID, 0, 0},
{
0,
}};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(pci, xlinux_id_table);
static struct pci_driver xlinux_driver = {
.name = "xlinux",
.id_table = xlinux_id_table,
.probe = xlinux_probe,
.remove = xlinux_remove,
};
static int __init xlinux_init(void) {
printk(KERN_INFO "init xlinux driver!\n");
return pci_register_driver(&xlinux_driver);
}
static void __exit xlinux_exit(void) {
printk(KERN_INFO "exit xlinux driver!\n");
pci_unregister_driver(&xlinux_driver);
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_VERSION("1.0");
module_init(xlinux_init);
module_exit(xlinux_exit);
|